Babylonian Empire
Babylonian Empire

(Text by Duane R. Hurst © 2013)
Click on a link to view its information and pictures.
|
BABYLONIA LINKS: Significant Event: Battle at Carchemish in 605 BC Code of Hammurabi Ishtar Gate in Babylon Main Cities: Babylon; Nippur Time: 1900-1100 BC Language: Akkadian Personage: Belshazzar; Hammurabi; Nebuchadnezzar Religion: Babylonian Gods Related Country: Iraq Brief History: I have included only a few items concerning the history of this empire. A good source for more details can be found on Wikipedia or in history books. |
|
|
Babylon was a small town in Mesopotamia that developed into a
large city and capital of the Babylonian empire. Its Tower of Etemenanki
may have seemed similar to the ancient Tower of Babel
(see alternate Picture).
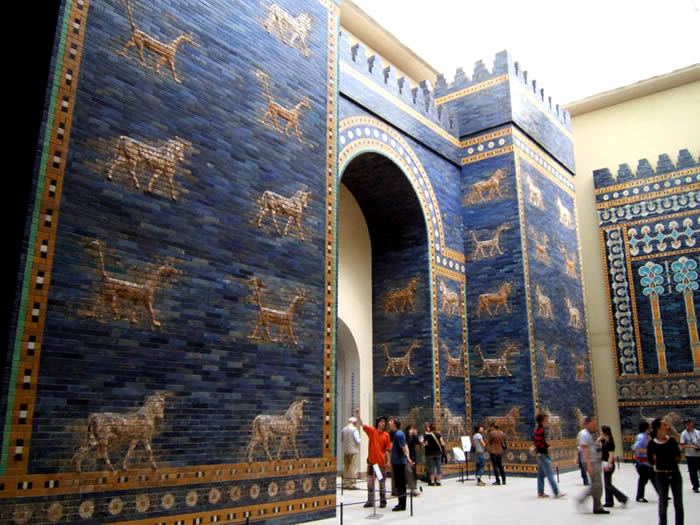
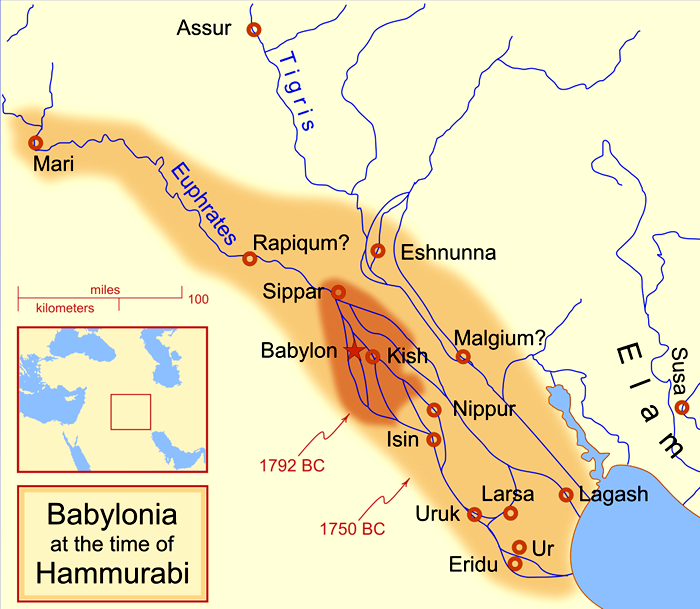
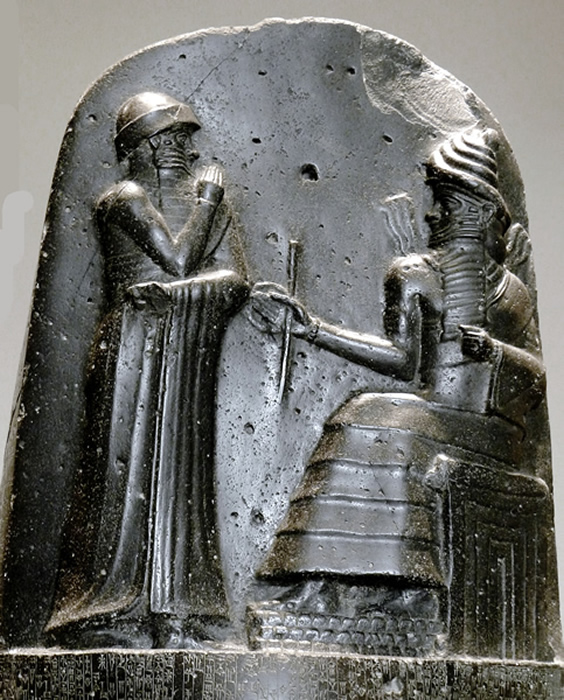
HAMMURABI: Hammurabi likely was called Amraphel, king of Shinar, in Genesis 14:1. He was the son of Sin-Muballit and became king circa 1792 BC. He also was the great lawgiver in ancient Babylon. The king of Larsa allied with Hammurabi to crush an invasion from Elam. Larsa's later duplicity resulted in Hammurabi conquering that kingdom and lower Mesopotamia by 1763 BC. Other conquests included: Amorites; Eshnunna; Mari. Hammurabi died in 1750 BC and left power to his son Samsu-iluna. ASSYRIAN PERIOD: Assyria conquered and ruled Babylonia between 911 and 605 BC. During the next 300 years the region experienced numerous rebellions and periods of peace. King Esarhaddon (681-669 BC) rebuilt the city of Babylon and gave Babylonia to his oldest son, Shamash-shum-ukin. The younger son, Ashurbanipal, received the more powerful Assyria. After decades of peace, Shamash-shum-ukin declared Babylon as capital of the empire. His brother responded to the powerful coalition of foes (Arabs; Arameans; Medes; Suteans) and eventually sacked Babylon. He destroyed Elam and subjugated the other people. Assyria later descended into chaotic civil war. NEO-BABYLONIA (CHALDEAN) PERIOD: (See Map of Neo-Babylonia.) Nabopolassar seized control over most Babylonian territory from Assyria in 620 BC. Assyrian resistance was considerable and resulted in an alliance between Nabopolassar and Cyaxares, king of Medes and Persians in 616 BC. Babylonian forces sacked the Assyrian capital at Nineveh. Pharaoh Necho II of Egypt belatedly sent an army to join with Assyrians to battle Nabopolassar's troops. However, Babylonia routed them at Carchemish. NEBUCHADNEZZAR II: Nebuchadnezzar was the oldest son of Nabopolassar and reigned from 605 to 562 BC. In 605 he defeated combined forces of Egypt and Assyria at the battle at Carchemish. His forces later conquered Judah and brought numerous captives to Babylon after they destroyed Jerusalem and Solomon's temple. Other conquests included: Egypt; Phoenicia; Syria; Tyre (negotiated alliance after a 13-year siege). Nebuchadnezzar rebuilt Babylon's great walls and constructed the fabled Hanging Gardens. The blue, glazed-tile Ishtar Gate was another famous landmark of the city (Another View). The Old Testament related various events between the king and Daniel the prophet. His son, Amel-Maruk, reigned after Nebuchadnezzer's death. The last king of Babylonia was Nabonidus in 539 BC. |
|
|
© Page Publisher: Duane R. Hurst
|