Viking Lands
Viking Lands

(Text by Duane R. Hurst © 2013)
Click on a link to view its information and pictures.
|
VIKING LINKS: Significant Event: Longhouse in Newfoundland Construction of Viking Ships Main Cities: Oslo; Trondheim; Visby Time: 790-1066 AD Language: Danish; Norwegian; Runic; Swedish Personage: Harald Fairhair; Harald Hardrada; Leif Ericson Religion: Viking Gods Related Country: Denmark; Norway; Sweden |
|
|
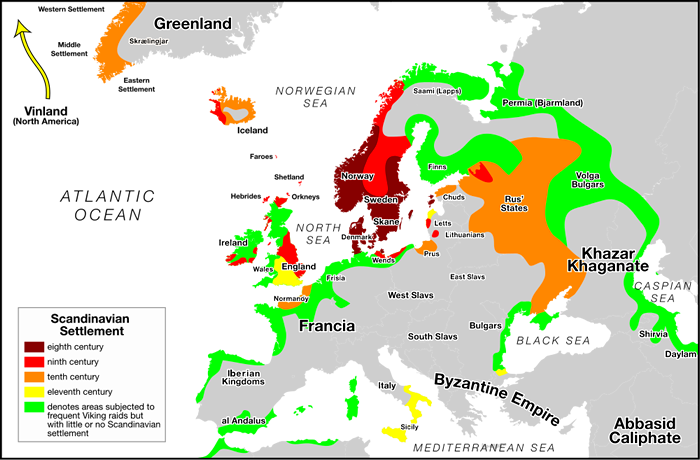
Brief History: I have included only a few items concerning the history of these people. A good source for more details can be found on Wikipedia or in history books. EARLY YEARS: "Viking" was an Old Norse feminine noun that meant taking an overseas expedition, usually in a Longship. Although Vikings certainly raided many locations previously, the Viking Era officially began with a raid at Lindisfarne Abbey on 8 June 793 AD. Vikings often raided soft targets or attempted trade with stronger locations. A harsh climate and marginal agriculture contributed to departure from villages on their viking quests. Common battle gear of a Viking Soldier included a round, wooden shield (often embossed with metal); heavy spear; throwing ax; helmet; and long sword. A standard method of fighting was the Shield Wall for defensive measures. Battles usually were confused melees. When a Viking chief died, he often was was buried or burned in a longship. EXPLORATION: Circa 825 AD, Gadded from Faeroes was the first Viking to discover Iceland (aka Öxney). Gunnbjörn Ulfsson discovered Greenland after his ship was blown off course when sailing from Norway to Iceland. This occurred nearly 100 years before Erik the Red first sighted Greenland in 982 AD. Circa 986 AD, Erik's son, Leif Ericson, and others briefly settled land they called Vinland ("land of meadows") in Newfoundland. Seemingly fragile Viking ships actually were superbly constructed and seaworthy craft. INVASIONS AND SETTLEMENTS: Vikings settled the Faeroes, Hebrides, Ireland, Isle of Man, Orkney Islands, Scotland and Shetland Islands. They also launched attacks against London. Between 859 and 862 AD, Hastein and Bjørn Ironside led 62 ships raided many Islamic cities, including Algeciras, Orihuela and Roussillon. After wintering on Camargue Island, they sacked towns in southern France and Luna on the Magra River, mistaking it for Rome. England: In 787 AD, three Viking ships from Norway raided Portland Bay. For many years thereafter, Vikings raided England for booty. In 865 AD, an army of Danish Vikings led by Guthrum, Halfdan and Ivar "the Boneless" Ragnarsson (Great Viking Army) invaded East Anglia. They conquered York and Mercia. In 871 AD, king Bagsecg brought reinforcements from Scandinavia. King Alfred the Great defeated the Danes at the Battle of Edington, but a treaty allowed them to control the Danelaw. Eric Bloodaxe led the last wave of invaders from Norway to England in 947 AD. He captured York, became king of Northumbria and probably ruled the Hebrides. France: In the mid 9th century AD, Vikings raided deep into Frankish territory. Viking leader Rollo besieged Paris (25 November 885 - October 886 AD). He received the Dutchy of Normandy from Charles III (aka Charles the Simple) as a bribe to withdraw. Later Norman (Viking) rulers expanded their territory. Ireland: Vikings founded many towns in Ireland, including Dublin and Limerick. In 832 AD, 120 Vikings ships under Turgesius invaded Ireland's eastern and northern coasts. Vikings established a base at Longphorts (Dublin) in 840 AD. Irish forced the Vikings out circa 900 AD, but they returned in 914 AD to establish a city at Waterford. The last battle between Vikings and Irish king, Brian Boru, was in 1014 AD at Clontarf. Russia: Vikings founded the Rus Khaganate in the late 8th century AD in northwest Russia. It likely was a group of associated city-states. A Viking leader, Oleg of Novgorod, later founded the Kievan Rus state in 882 AD. They abandoned the old gods after Vladimir Svyatoslavovich (980-1015 AD) ordered his subjects to accept Christianity. Scotland: Vikings ruled the fringe of Scotland (including the Hebrides, Orkney and Shetland islands) between the 8th and 15th centuries AD. They also settled on the Isle of Man. Early settlers arrived on the Shetland island of Unst in the mid 7th century AD. Vikings fought local forces from various kingdoms of the Picts. Many foes settled in distant islands as they fled Norway to escape retribution from king Harald Fairhair in 872 AD. However, Fairhair pursued them and incorporated the Scottish Viking islands into his kingdom in 875 AD. Remains of Viking settlements abound, such as at Brough of Birsay in the Orkneys. Viking settlements spurred the Picts and Scots to unite under the rule of king Cínaed mac Ailpín in the mid 800s AD. END OF AN ERA: The last Viking battle in Norway was at Stiklestad on 29 July 1030 AD. King Olaf II died and Harald Sigurdsson (aka Harald Hardrada) fought in the battle. Prior to a harsh reign (1046-1066 AD) over the Norse kingdom, Hardrada was head of the Varangian Guard at Constantinople. Under encouragement from Tostig Godwinson, Hardrada landed an army in Northumbria to seize kingship from Harold Godwinson. Hardrada died in the Battle of Stamford Bridge on 25 September 1066 AD. Godwinson, another "Viking" ruler, died on 14 October 1066 AD at the Battle of Hastings. |
|
|
© Page Publisher: Duane R. Hurst
|